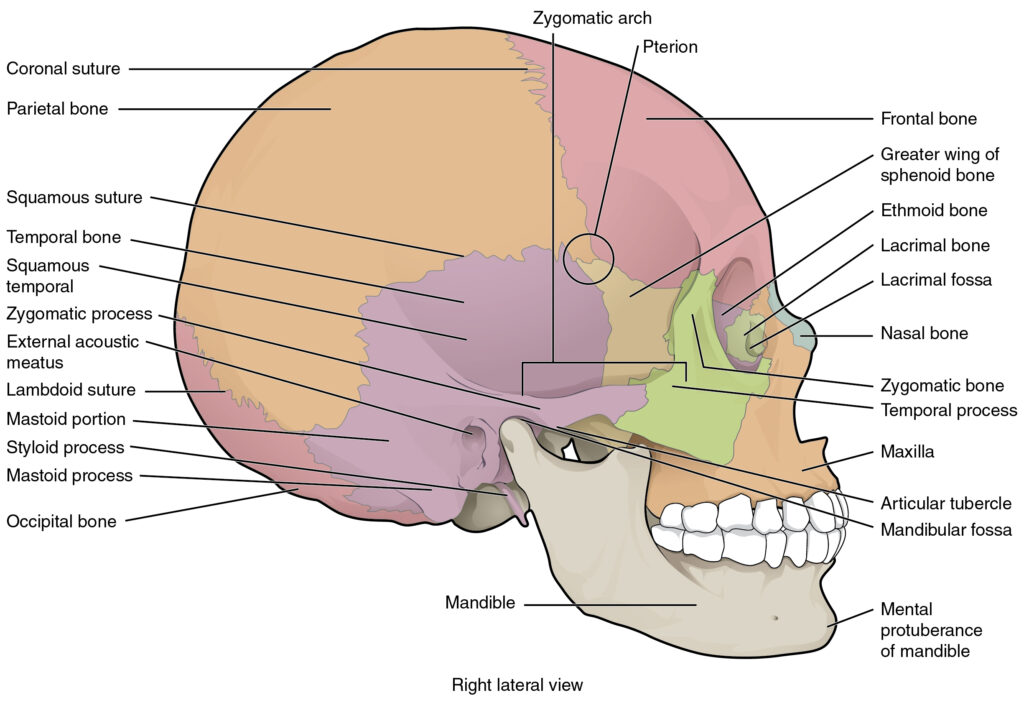
Key anatomical features of the skull include various structures and functions.
Temporal Bones:
The bones located on the lateral sides of the skull, known as the temporal bones, house and protect the delicate structures of the middle ear, which are essential for hearing.
Foramen Magnum:
A large and critical opening located at the base of the skull, known as the foramen magnum, serves as the point where the spinal cord connects to the brain, facilitating essential communication between these two vital structures.
Sphenoid Bone:
A complex and intricately shaped bone that forms the base of the skull, known as the occipital bone, connects to many other cranial bones, playing a vital role in providing stability and structure to the skull.
Parietal Bones:
Two large bones that together form the sides and the top of the cranium are known as the parietal bones, which provide structural support and protection for the brain.
Occipital Bone:
The posterior region of the skull, which houses the foramen magnum, serves as a crucial opening for the spinal cord.